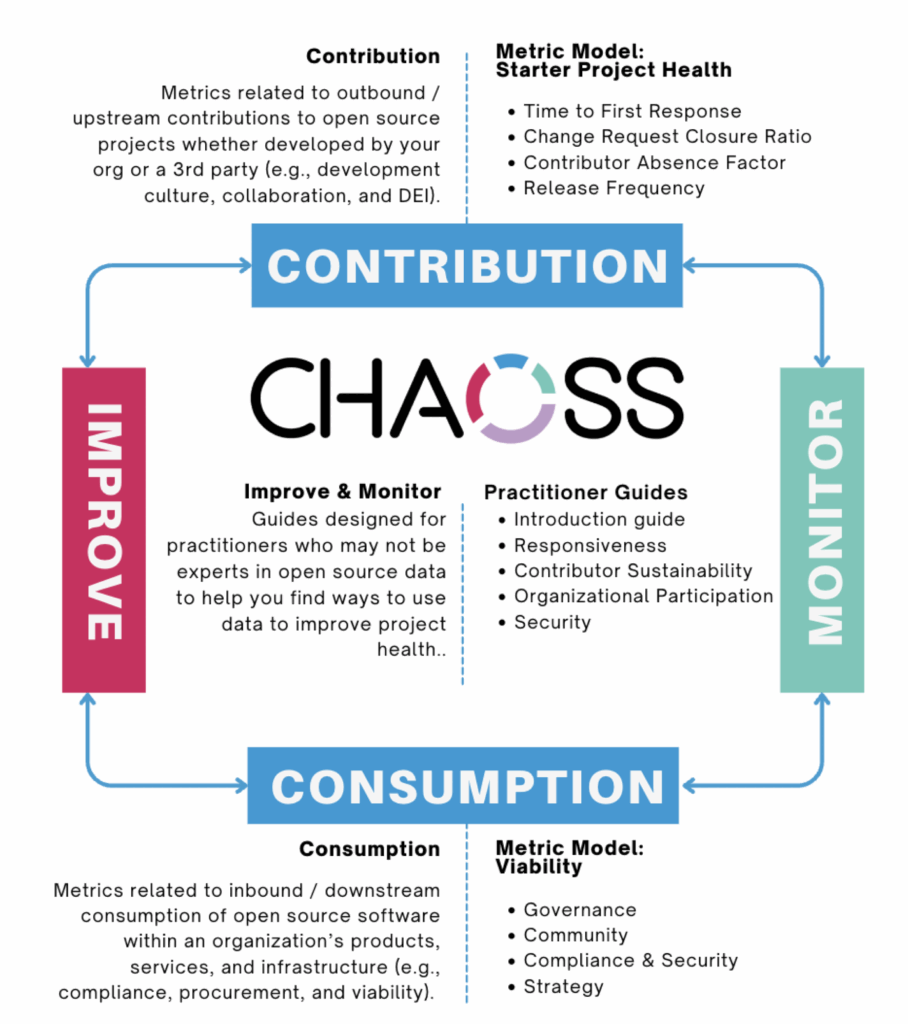
Open source sustainability impacts all of us, and unfortunately, we know that many open source projects are struggling. Maintainers are experiencing burnout, lack of funding, and a general lack of resources to sustain their projects over the long term. This is something that was top of mind for me while I was in Brussels for CHAOSScon EU, the Open Forum Europe (OFE) Summit, and FOSDEM.
At CHAOSScon, during the opening session, I talked about demonstrating the value of open source efforts with a focus on how to articulate the value within organizations so that the open source work can continue over time (slides), which is one aspect of sustainability that I’ve already talked about here on this blog.
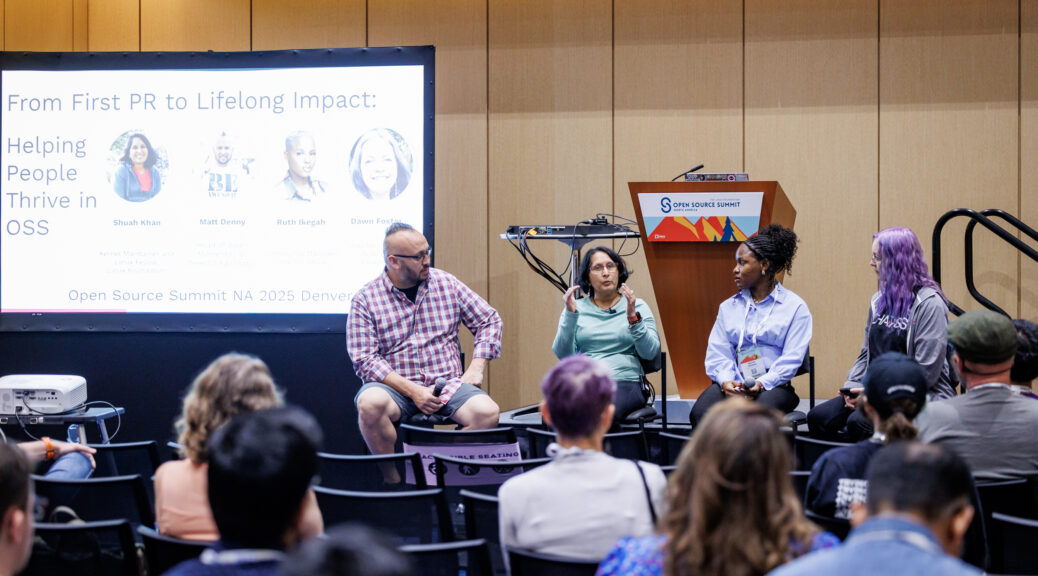
We also had a fishbowl panel all about funding for open source projects to wrap up the day at CHAOSScon. The funding panel covered a wide variety of topics, so here are just a few topics mentioned by the panelists:
- Past vulnerabilities can be used to make the case for future funding (e.g., Germany’s Sovereign Tech Fund)
- Money isn’t something that all open source maintainers want to spend time thinking about, and it can be a problem for communities to decide who gets funding?
- We need more recognition by policy makers about the value of open source and need to revamp procurement to make it easier to use public money to fund open source.
- Funders need to understand the impact of their funding, but many corporate FOSS funders programs don’t have a focus on understanding and measuring impact.
- Funding can be exploited when it’s not well-defined, and this can happen when people who aren’t particularly familiar with open source (e.g., policy, regulators, legal folks) are defining these programs.
- Open Source Wishlist is an effort that Emma Irwin has been working on to bridge the gap between maintainers, funders, and practitioners.
I also attended several sessions in the FOSDEM Funding Devroom. Luckily, all of the devroom talks are recorded, since I wasn’t available to watch every talk, but I did pick up a few interesting tidbits from the talks that I did attend:
- When measuring funding impact, quantitative data can help support credibility claims, but you also need qualitative data with narratives that carry meaning.
- Human sustainability is harder to measure than infrastructure impact, but maintainer health is a critical blind spot that should also be considered when making funding decisions.
- Short term deliverables dominate impact measurement while long-term sustainability is undervalued because success often looks like nothing happened.
- Funding impact isn’t neutral. Funders’ visions shape everything: what / who gets funded, how impact is measured, and how work is valued. Funding from companies can bias development toward corporate interests.
- Funders often use a trust model where they fund people, projects, and organizations they trust, but that’s fragile because it’s personal, and people change roles. This is also hard to scale and creates bottlenecks.
- Funders often struggle to provide funding to individuals, since it’s often easier to fund projects or organizations.
- Funding can be a time consuming and ongoing process for maintainers and projects to continue to find more funding when one wave of funding ends.
- It can also be hard for funders to work together to align processes and goals to create joint funding efforts.
Seeing more people talking about funding was great, and I really appreciated the thoughtful approach from several of the speakers about how funding isn’t a panacea. Funding doesn’t solve all of our sustainability issues, but it is one important tool that can help projects improve sustainability. If you are interested in learning more, we have a CHAOSS Funding Impact Measurement Working Group that meets every other Wednesday, and I am also available for consulting on this topic.
Related Resources:
- The Impact of Funding for Sustainable Open Source Projects
- Sustainable Open Source Leadership
- From Data to Action: Building Healthy and Sustainable Open Source Projects
- Contributor Sustainability Impacts Risk and Adoption of OSS Projects
- What can your OSPO do about power dynamics, rug pulls, and other corporate impacts on OSS sustainability?
- CHAOSScast Episodes on Demonstrating Value and Funding Impact
- FOSDEM Funding Devroom – videos will be available for all talks
Photo by micheile henderson on Unsplash